
When you make a request to a server and everything seems technically correct, the URL exists, the server is reachable, it can still happen that you receive an error message. An example of this is the 405 error: Method Not Allowed.
This message means that the server has received the request but does not allow the HTTP method used (such as GET, POST or PUT) for the specific endpoint you are trying to contact. In other words, you are trying to perform a valid action, but in a way that is denied by the server.
The error message occurs frequently when working with APIs, dynamic routes or form submissions, and can be confusing at first. Everything seems to be in place to successfully interact with the server, yet you still don't get a proper response back. In this article, we explain exactly what the http 405 error means, why it occurs, and how to fix the problem.
What is status code 405?
The 405 status code comes from the HTTP protocol and literally means: Method Not Allowed. Not because you are wrong with the URL, or because the page does not exist (as in a 404), but because the way you are trying to request something is not allowed.
So it is not in what you request, but in how you do.
In practice, this usually means that you send, for example, a POST or PUT request to an endpoint that only accepts GET. The server knows the method, it just refuses it for that particular route. And it refuses it on purpose.
In response, you then often see something like:
HTTP/1.1 405 Method Not Allowed
Allow: GET, HEAD
That Allow header is crucial. It tells you which methods are allowed for this resource. No POST? Then the answer is simple: you are not allowed to post here. Period.
How does a 405 error message occur?
There is no single cause for an http 405. But there are a few usual suspects you should always check.
Sometimes it's as simple as a front-end form that sends a POST to a route that only accepts GET. Sometimes it is deeper: a server configuration, an error in routing, or an API that is not properly configured.
Are you working with a framework? Then it might as well be a route that does not allow PUT while you are trying to. And do you use WordPress or another CMS? Then a security plugin can block certain methods.
Typical scenarios:
- You send a POST to a static HTML file
- Your API only accepts GET and HEAD, but you send PUT
- Your firewall sees a DELETE and intervenes
- Your server is misconfigured and blocking methods via .htaccess or Nginx rules
In short: the request arrives. But is deliberately denied.
Solving 405 status code: what can you do?
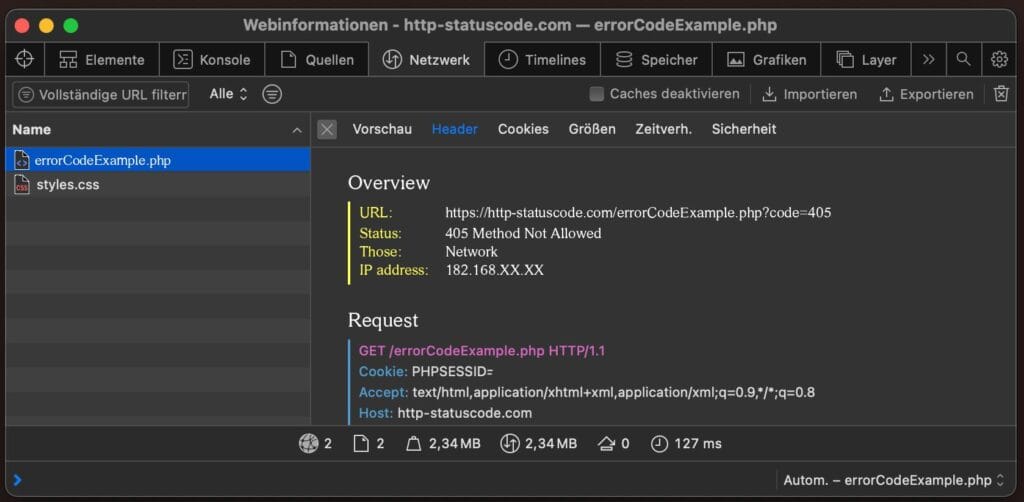
The error message itself says little, but the solution is often technically easy to trace. Start with the method you are using. Ask yourself: is this method allowed for this route? And if not: why not?
Here are five methods to tackle status code 405 method not allowed:
1. Check the HTTP method used
Are you using the right method for this route? Not every endpoint accepts POST, PUT or DELETE. Sometimes GET is the only option. Use Postman, curl or the browser dev tools to see exactly what you are sending, and what the server is returning. Especially look at the Allow header in the response. It tells you what is allowed.
2. Inspect your routes or endpoint configuration.
In backend frameworks such as Laravel, Express, Rails or Django, routes must explicitly accept methods. If your route /products only accepts GET, you will get a 405 when you try to POST. Just checking in your router or controller file can clear up a lot.
3. Review your server or .htaccess configuration
On Apache systems, you can block methods via .htaccess with a Limit directive. In Nginx, this is via limit_except. An incorrectly set rule can block legitimate requests. Taking a moment to dive into the server configuration definitely pays off here.
4. Temporarily disable plugins or firewalls
With CMSs such as WordPress or Joomla, a security plugin can block methods without you noticing. Especially DELETE, PUT or even PATCH can be flagged as suspicious behavior. Temporarily disable your plugins, test again, and see if the error disappears.
5. Analyze the request headers
Use your browser's developer console or a tool like curl. Look at the request and response headers. Are you sending everything correctly? And what does the Allow header say? Sometimes the server indicates exactly what you are allowed to do. That makes debugging a lot easier.
In conclusion
A 405 method not allowed is technically a neat error. Everything works except the method. That also makes it frustrating. Especially if you think the endpoint is just fine, or you don't have access to the server config.
Whatever it is: the 405 is not a bug. It is a limitation. A limitation. And your job is to figure out where that limit is, and why you're running into it.
So do you see a 405 error? Then don't wonder or you're doing something wrong, but what you're trying to do, and whether that's allowed at all.